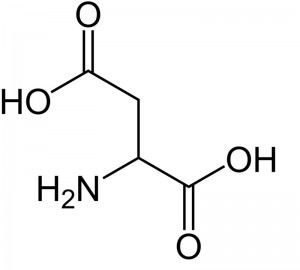
| CAS Number | 56-84-8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 133.103 |
| InChI Key | CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N |
| LogP | -3.89 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of Aspartic Acid
July 10, 2024
Access the UV-Vis Spectrum SIELC Library
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Aspartic Acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.

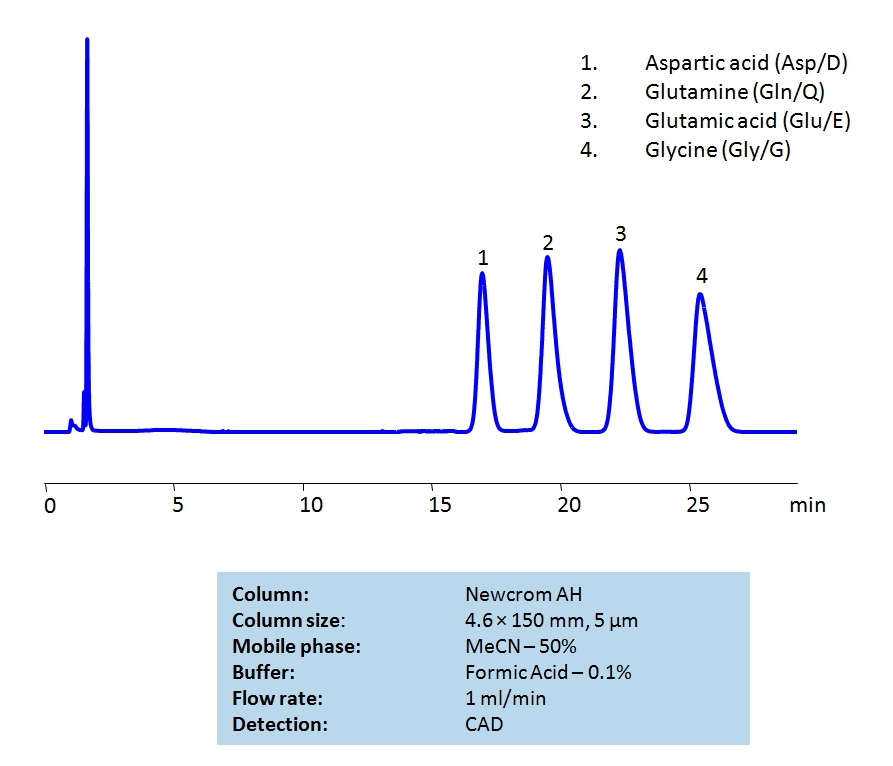
HPLC Separation of Amino Acids on Newcrom AH Column
October 1, 2020
HPLC Method for Aspartic Acid, L-Glutamine, Glutamic Acid, Glycine on Newcrom AH by SIELC Technologies
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Based on their dietary requirement, they are classified into essential and non-essential amino acids. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the human body in sufficient quantities and must be obtained from the diet. Non-essential amino acids, on the other hand, can be synthesized by the body and are not dependent on dietary intake.
It’s worth noting that while these amino acids are considered “non-essential” for adults under normal circumstances because the body can synthesize them, there are situations where some may become “conditionally essential.” This means that under certain conditions like illness, stress, or trauma, the body might not produce them in sufficient quantities, and dietary intake becomes necessary. Arginine, for instance, is considered conditionally essential, especially during periods of rapid growth, illness, or trauma.
You can find detailed UV spectra of Aspartic Acid and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
You can find detailed UV spectra of Glutamine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
You can find detailed UV spectra of Glutamine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
You can find detailed UV spectra of Glutamine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Aspartic Acid, L-Glutamine, Glutamic Acid, Glycine can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom AH stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a Formic Acid buffer. Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 50% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic Acid, L-Glutamine, Glutamic Acid, Glycine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Glutamic Acid
Glycine
L-Glutamine

HPLC Separation of a Mixture of Non-Essential Amino Acids, such as L-Aspartic Acid, L-Serine, L-Glutamic Acid, and L-Alanine on Primesep 100 Column
March 11, 2019
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Non-Essential Amino Acids on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
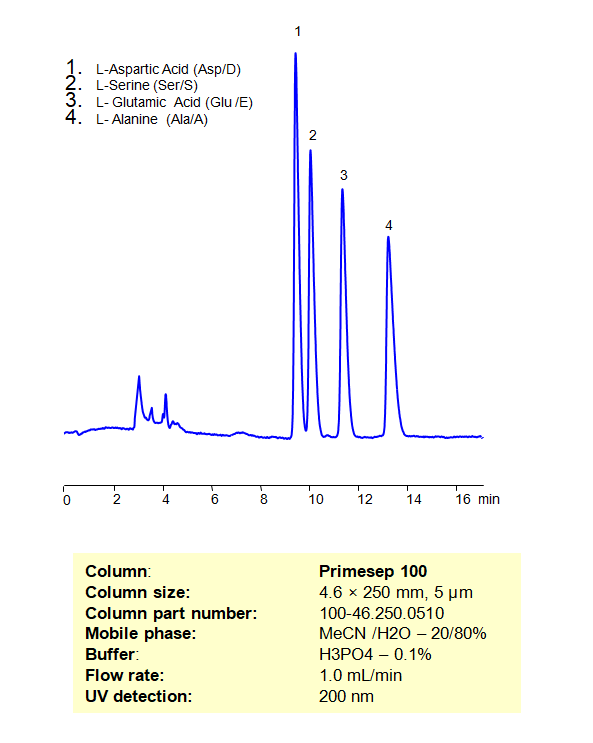
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Non-Essential Amino Acids
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic Acid, Serine, GLU (L-Glutamic acid), Glutamic Acid, D-Alanine, DL-Alanine, Amino Acids, Alanine |
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Based on their dietary requirement, they are classified into essential and non-essential amino acids. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the human body in sufficient quantities and must be obtained from the diet. Non-essential amino acids, on the other hand, can be synthesized by the body and are not dependent on dietary intake.
It’s worth noting that while these amino acids are considered “non-essential” for adults under normal circumstances because the body can synthesize them, there are situations where some may become “conditionally essential.” This means that under certain conditions like illness, stress, or trauma, the body might not produce them in sufficient quantities, and dietary intake becomes necessary. Arginine, for instance, is considered conditionally essential, especially during periods of rapid growth, illness, or trauma.
Amino acids can be retained, separeted and analyzed on a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a phosphoric acid (H3PO4) as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected in the UV regime at 200 nm.
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Amino Acids
Aspartic Acid
D-Alanine
DL-Alanine
GLU (L-Glutamic acid)
Glutamic Acid
Serine

HPLC Separation of Lysine and Arginine from Other Amino Acids
July 10, 2012
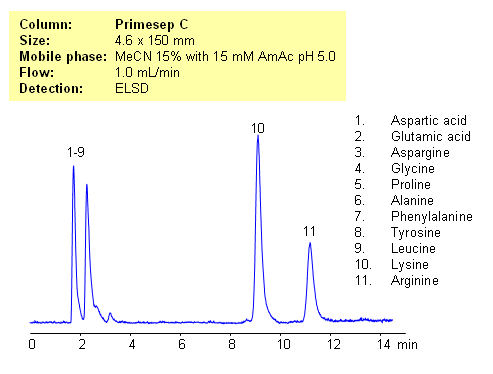
Application Notes: Amino acids are polar ionic compounds which are not retained on reversed-phase column without ion-pairing reagent. In our application, lysine and arginine can be separated from other amino acids. Amino acids with a pH between 3 and 5 and with one basic and one acidic group become very polar. Therefore these amino acids don’t have strong ion-exchange interaction with Primesep C stationary phase. Amino acids with two amino groups still carry positive net charge and can interact with stationary phase by cations-exchange mechanism. pH variation of the mobile phase can be an effective tool to adjust selectivity of separation for zwitter-ionic, basic and acidic compounds. This method can be used for separation of mono-charged compounds from compounds having an extra charge.
Application Columns: Primesep C
Application compounds: Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Aspargine, Glycine, Proline, Alanine, Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Leucine, Lysine, Arginine
Detection technique: UV, LC/MS, ELSD/CAD
| Column | Primesep C, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 15% |
| Buffer | AmAc pH 5.0- 15 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Aspargine, Glycine, Proline, Alanine, Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Leucine, Lysine, Arginine |
Application Column
Primesep C
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsArginine
Asparagine
Aspartic Acid
Glutamic Acid
Glycine
Leucine
Lysine
Phenylalanine
Proline
Tyrosine
UV Detection

HPLC Separation of Aspartic Acid and Asparagine on Obelisc R Column
October 4, 2010
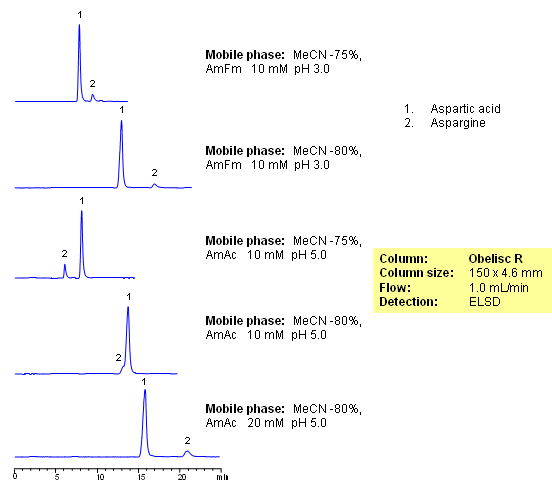
Two amino acids, aspartic acid and asparagine, are separated on an Obelisc R column by combination of reverse-phase and ion-exchange mechanism. Method can be used for analysis of these and other underivatized amino acids by HPLC with UV, ELSD, CAD and LC/MS detection.
| Column | Obelisc R, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm, AmAc |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Asparagine, Aspartic Acid |
Application Column
Obelisc R
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsAspartic Acid

Effect of Both pH and Organic Content on a Separation of Sugars, Amino Acids, and Carboxylic Acids
March 3, 2010
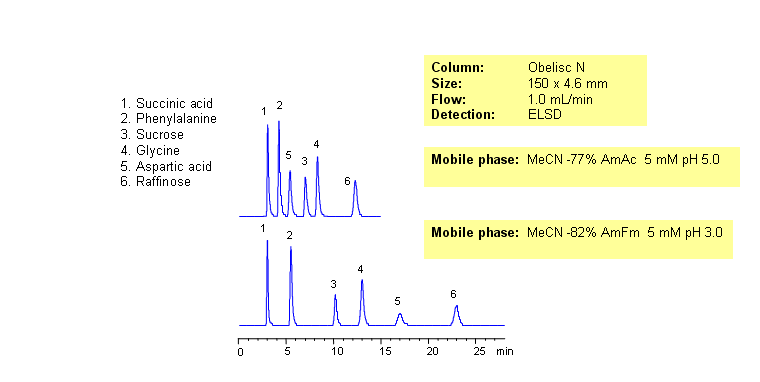
In mixed-mode HILIC chromatography, selectivity of separation can be adjusted by amount of acetonitrile, amount of buffer and buffer pH. Buffer concentration and pH will affect retention of ionizable compounds to a different degree. Retention of neutral compounds can be adjusted by the amount of acetonitrile. Carboxylic acid, three amino acids and two sugars are separated by combination of HILIC and ion-exchange mechanisms. Compounds can be monitored by ELSD, Corona (CAD), LC/MS or low UV. UV-transparent mobile phase /buffer is required for UV monitoring of this mixed-mode separation. This HPLC method can be adopted as general approach for analysis of sugars, amino acids and carboxylic acids.
| Column | Obelisc N, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmAc |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Succinic Acid, Phenylalanine, Sucrose, Glycine, Aspartic Acid, Raffinose |
Application Column
Obelisc N
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Phenylalanine
Raffinose
Succinic Acid
Sucrose

HPLC Separation of Polar Compounds
January 13, 2010
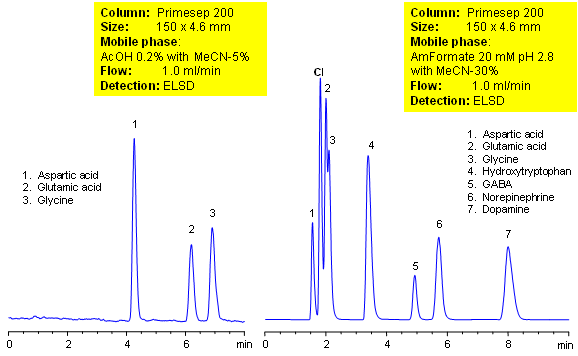
The separation of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, can be challenging to separate on a reverse-phase column due to their high polarity. Using a mixed-mode HPLC column, allows the separation of amino acids by cation-exchange and ion-exclusion mechanisms as well as hydrophobicity. Fine tuning of separation can be achieved with changes in organic concentration of the mobile phase as well as choice of buffer and pH.
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AcOH, AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Hormone |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic acid, Glutaric acid, Glycine, Hydroxytriptophan, GABA, Norepinephrine, Dopamine |
Application Column
Primesep 200
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsAspartic Acid
Dopamine
Glutamic Acid
Norepinephrine
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)

HPLC-ELSD Method for Analysis of Amino Acids on Primesep 100 Column
September 18, 2006
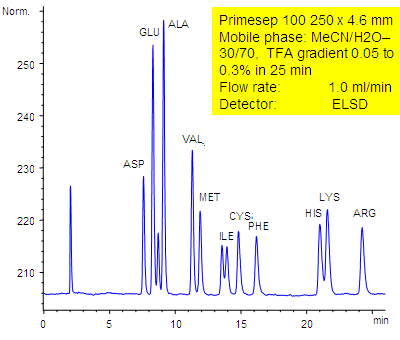
11 underivatized amino acids (aspartic acid, glutamic acid, alanine, valine, methionine, isoleucine, cysteine, phenylalanine, histidine, lysine, and arginine) are separated by a Primesep 100 HPLC column by reversed-phase and ion-exchange mechanisms with LC/MS compatible conditions without the use of ion-pair reagents. The HPLC separation uses a TFA (trifluoroacetic acid) gradient in a mobile phase of water acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN with evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD).
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6×250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 30/70% |
| Buffer | TFA , gradient 0.05-0.3 % , 25 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Alanine, Valine, Methionine, Isoleucine, Cysteine, Phenylalanine, Histidine, Lysine, Arginine |
Application Column
Primesep 100
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsAmino Acids
Arginine
Aspartic Acid
Cysteine
Glutamic Acid
Histidine
Isoleucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Valine

Bufferless Ion Separation (BLIS™) Chromatography of Amino Acids (2)
January 30, 2005
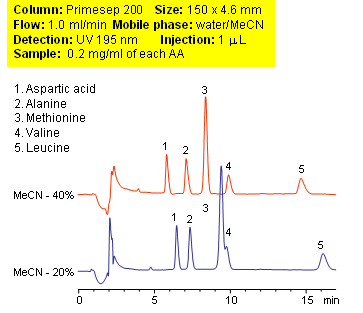
Adding on to the previous HPLC separation of amino acids using Bufferless Ion Separation (BLIS) Chromatography; here we have additional amino acids separated on Primesep 200 column using only water and acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN) in the mobile phase. Primesep 200 is a reverse-phase (RP) column with weak acidic ion-pairing groups embedded. With no buffer present in the mobile phase, detection can be achieved with UV, mass spectrometry (MS), evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD).
| Column | Primesep 200, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | No |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 195 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Aspartic acid, Alanine, Valine, Methionine, Leucine |
Application Column
Primesep 200
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsAmino Acids
Aspartic Acid
Leucine
Methionine
Valine