| CAS Number | 63449-41-2 |
|---|---|
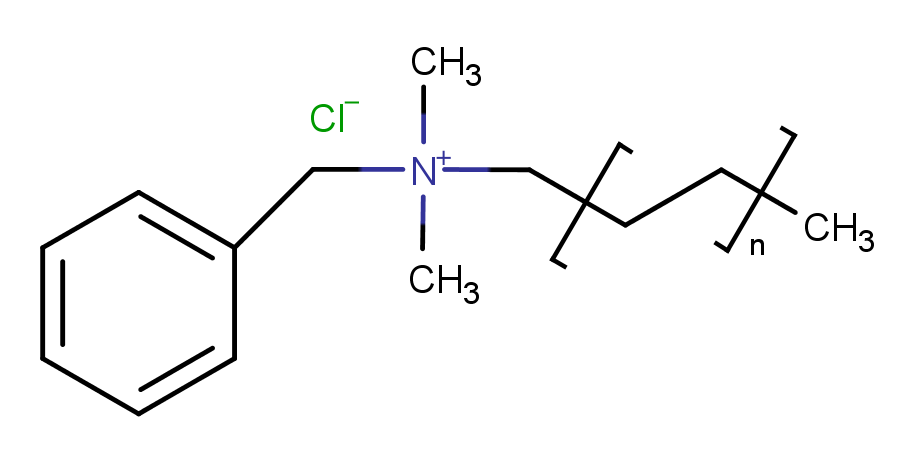
| Molecular Formula | C6H5CH2N(CH3)2RCl |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC MS Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium Chloride on Primesep SB Column
February 2, 2024
HPLC Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride on Primesep SB by SIELC Technologies
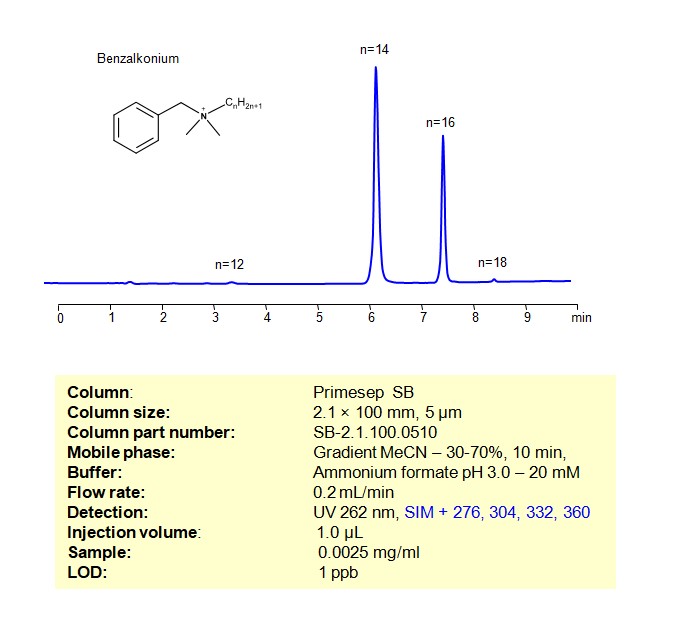
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride
Benzalkonium chloride is a quaternary ammonium compound and belongs to the class of chemicals known as cationic surfactants. It is often used as a disinfectant, antiseptic, and preservative in various products, including pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and surface disinfectants.
Function: It has antimicrobial properties and is effective against bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It disrupts the cell membranes of microorganisms, leading to their inactivation.
Common Uses:
- Disinfection of surfaces in healthcare settings.
- Preservative in ophthalmic solutions and nasal sprays.
- Ingredient in some antiseptic wipes and hand sanitizers.
- Preservation agent in various personal care products.
Variants: There are different variants of Benzalkonium chloride with varying alkyl chain lengths, and the specific composition may affect its properties and applications.
Benzalkonium can be retained, and analyzed using a Primesep SB mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a gradient method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium formate as a buffer. Detection is achieved using UV and LC MS positive mode
| Column | Primesep SB, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 30 – 70%, 10 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 40 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2ml/min |
| Detection | UV 262 nm, SIM + 276, 304, 332, 360 |
| Samples | 0.0025 mg/mL in MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD* | 1 ppb |
| Class of Compounds | Alkaloid, Quaternary ammonium |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium chloride |
Application Column
Primesep SB
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
LC MS Detection

HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH Column
July 10, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Surfactants, also known as surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension (or interfacial tension) between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants.
They are often classified according to the charge of the polar head group:
Anionic Surfactants: These surfactants have a negative charge on their polar head group. Common examples include soap, sodium laureth sulfate, and sodium lauryl sulfate. They are commonly used in detergents and shampoos due to their ability to emulsify oils and hold dirt in suspension, so it can be rinsed away.
Cationic Surfactants: These surfactants have a positive charge on their polar head group. Examples include cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and benzalkonium chloride. These are often used as antiseptics and can also be found in hair conditioners because they reduce static cling.
Nonionic Surfactants: These surfactants have no charge on their polar head group. Examples include alcohol ethoxylates, nonylphenol ethoxylates, and polysorbates. Nonionic surfactants are often used in laundry and dishwasher detergents.
All compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a reverse-phase Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Ammonium formate, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
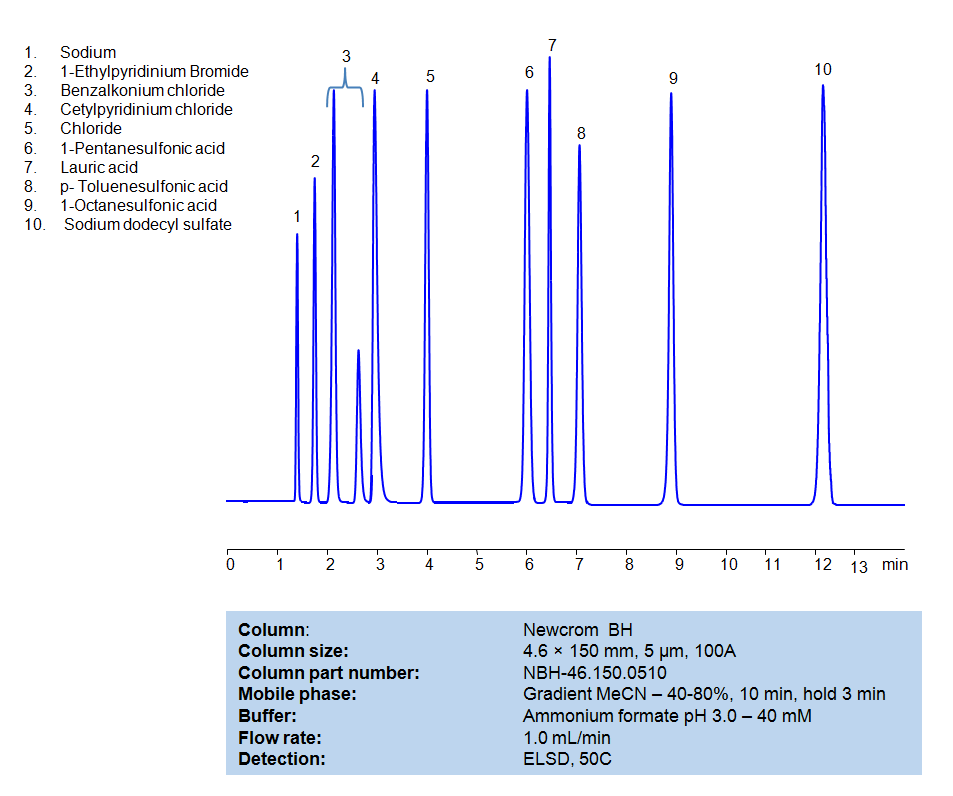
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid), p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA), 1-Octanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN -40-80%, 10 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 40 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 50C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Surfactants |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid), p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA), 1-Octanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Ethylpyridinium bromide |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
1-Octanesulfonic acid
1-Pentanesulfonic acid
Benzalkonium chloride
Cetylpyridinium Chloride
Dodecanoic acid (Lauric acid)
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)

HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic, Nonionic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH Column
July 10, 2023
HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrophobic, Cationic, Nonionic and Anionic Surfactants on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Surfactants, also known as surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension (or interfacial tension) between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants.
They are often classified according to the charge of the polar head group:
Anionic Surfactants: These surfactants have a negative charge on their polar head group. Common examples include soap, sodium laureth sulfate, and sodium lauryl sulfate. They are commonly used in detergents and shampoos due to their ability to emulsify oils and hold dirt in suspension, so it can be rinsed away.
Cationic Surfactants: These surfactants have a positive charge on their polar head group. Examples include cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and benzalkonium chloride. These are often used as antiseptics and can also be found in hair conditioners because they reduce static cling.
Nonionic Surfactants: These surfactants have no charge on their polar head group. Examples include alcohol ethoxylates, nonylphenol ethoxylates, and polysorbates. Nonionic surfactants are often used in laundry and dishwasher detergents.
All compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a reverse-phase Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Ammonium formate, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
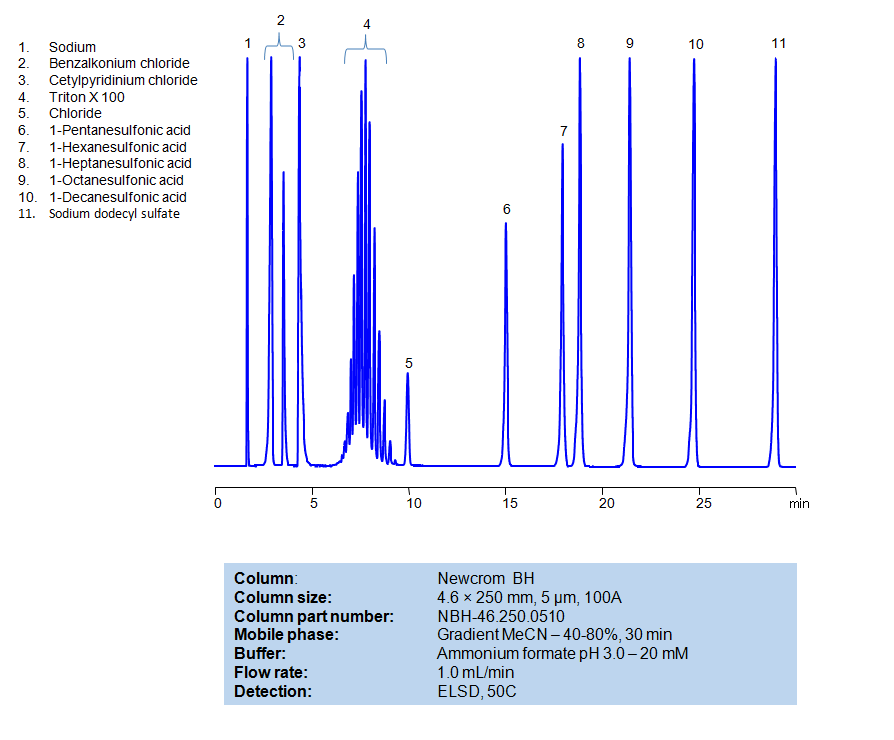
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, Triton X100, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, 1-Hexanesulfonic acid, sodium salt, 1-Heptanesulfonic acid, 1-Decanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Octanesulfonic acid
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN -40-80%, 30 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 50C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Aliphatic sulfonic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, Triton X100, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, 1-Hexanesulfonic acid, sodium salt, 1-Heptanesulfonic acid, 1-Decanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Octanesulfonic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
1-Heptanesulfonic acid
1-Hexanesulfonic acid, sodium salt
1-Octanesulfonic acid
1-Pentanesulfonic acid
Benzalkonium chloride
Cetylpyridinium Chloride
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
Triton X100

HPLC Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium Chloride on Primesep SB Column
February 8, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride on Primesep SB by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
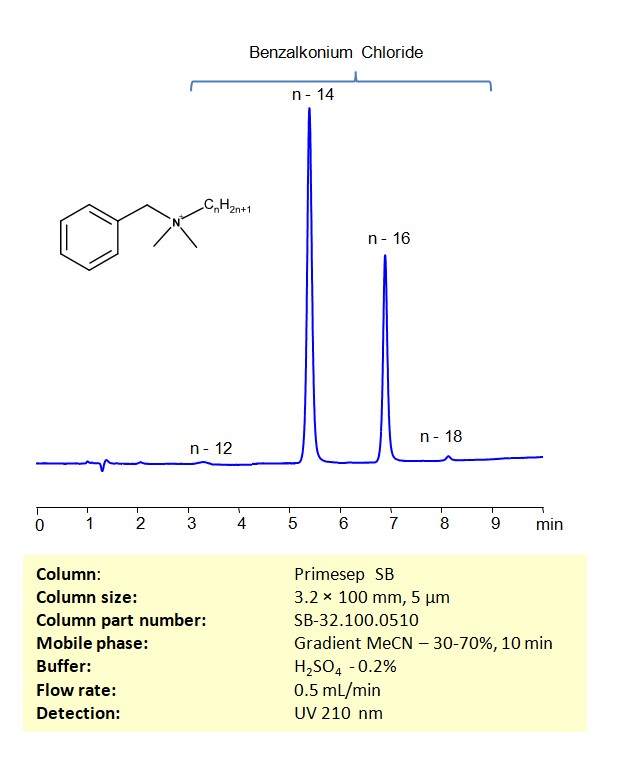
Benzalkonium chloride, also known as Zephiran or Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride, is a positively charged surfactant often used as a pharmaceutical preservative and as an antiseptic. Benzalkonium Chloride can be retained on a mixed-mode stationary phase Primesep SB column with embedded strong basic ion-pairing groups, using a gradient analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) ionic modifier. This analysis method can be UV detected at 210 nm with high resolution and peak symmetry.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride
Condition
| Column | Primesep SB, 3.2 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 30-70%, 10 min |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 210 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 5.32, 6.93 |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium chloride |
Application Column
Primesep SB
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Separation of Benzalkonium Chloride BCT 8358 on Primesep D column
July 8, 2011
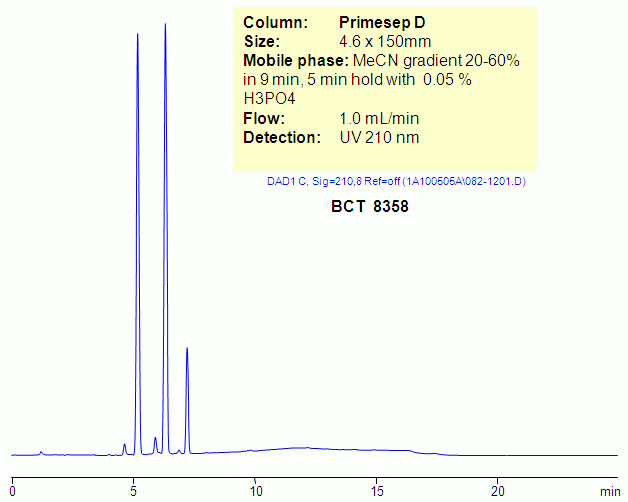
Benzalkonium chloride is a mixture of alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chlorides of various even-numbered alkyl chain lengths. It is used as a surfactant. Hydrophobic quaternary amines, like BTC, produce poor peak shape in reversed-phase chromatography due to interaction of quaternary amines with residual silanols. Ideal peak shape can be achieved on reversed-phase anion-exchange columns like Primesep D. Primesep D has a basic group on the surface of silica gel that shields silanols from interacting with quaternary, tertiary, secondary and primary amines. This allows to achieve symmetrical peaks for hydrophobic basic analytes. Compounds need to be hydrophobic enough to get compensation for repulsion effect coming from stationary phase. BTC can be monitored by ELSD and UV. Primesep D will also retain acidic counter-ions of quaternary amines, so simultaneous analysis of hydrophobic basic and hydrophilic basic compounds is possible.
| Column | Primesep D, 4,6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | H3PO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | 210 |
<
| Class of Compounds |
Surfactant, Hydrophobic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium Chloride BCT 8358 |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select options