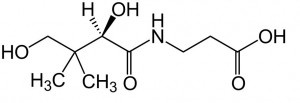
| CAS Number | 79-83-4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H17NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 219.237 |
| InChI Key | GHOKWGTUZJEAQD-ZETCQYMHSA-N |
| LogP | -1.1 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
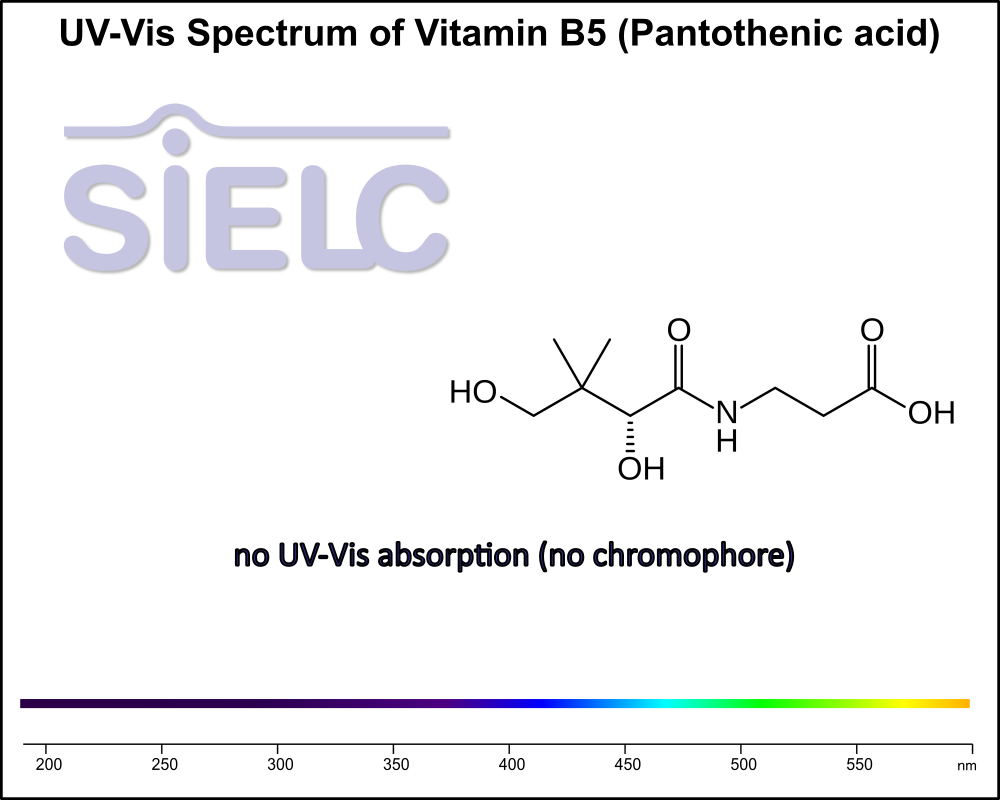
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
January 26, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze , Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.
Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)

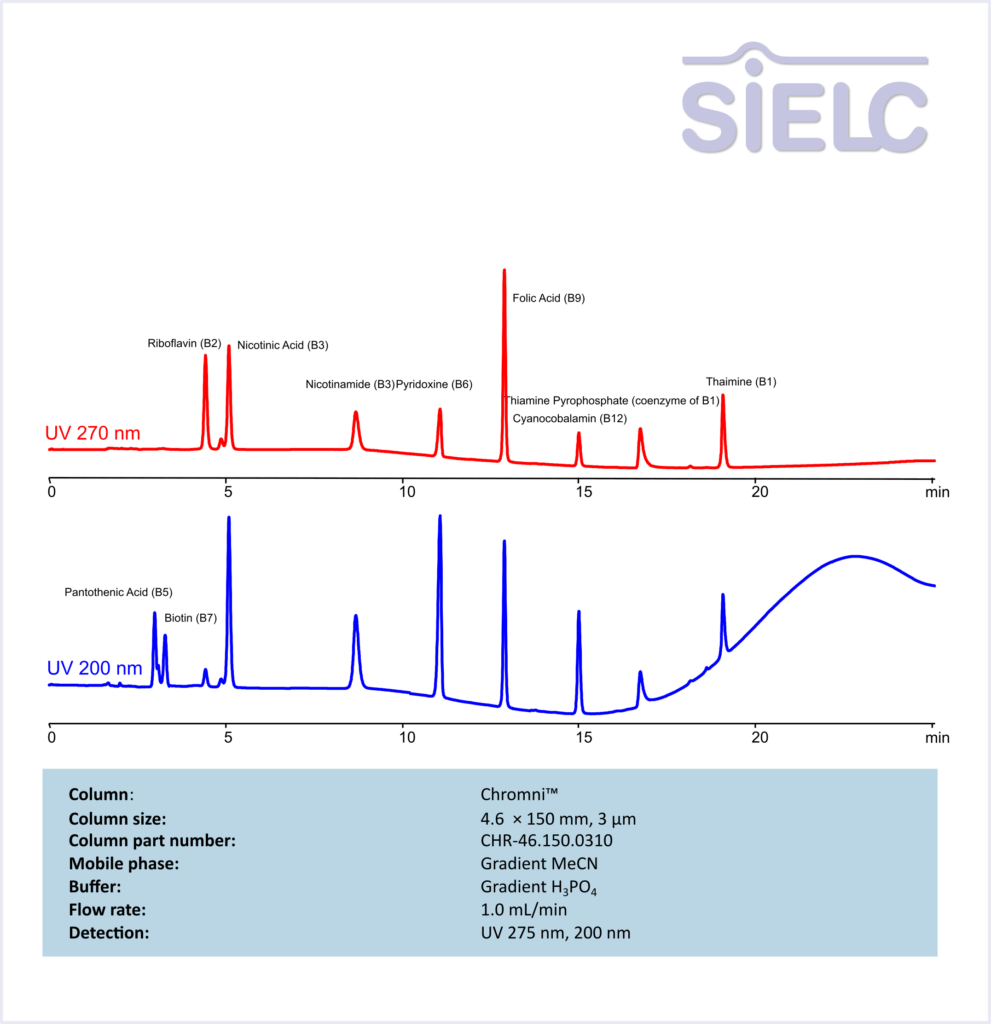
HPLC Method for Separation of 10 Water-Soluble Vitamins on Chromni Column
September 17, 2025
HPLC Method for Separation of 10 Water-Soluble Vitamins on Chromni by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for separation of Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid), Nicotinamide, Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine), Folic Acid, Cyanocobalamin, Thiamine diphosphate (Thiamine pyrophosphate), Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5), Biotin
Riboflavin (B2), Nicotinic Acid (B3), Nicotinamide (B3), Pyridoxine (B6), Folic Acid (B9), Cyanocobalamin (B12), Thiamine Pyrophosphate (coenzyme of B1), Thiamine (B1), Pantothenic Acid (B5), Biotin (B7) are water soluble vitamins with a key function of energy metabolism. These coenzymes are responsible for converting food into usable energy.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid), Nicotinamide, Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine), Folic Acid, Cyanocobalamin, Thiamine diphosphate (Thiamine pyrophosphate), Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5), Biotin can be retained and analyzed using the Chromni stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a gradient method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN). Detection is performed using UV.
| Column | Chromni, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – see table |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – see table |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 275 nm, 200 nm |
Gradient Elution Program for HPLC Method
| Time (min) | A – H2O (%) | B – MeCN (%) | C – H3PO4 1% in H2O (%) | Notes |
| 0 | 0 | 90 | 10 | Starting Conditions (Hold) |
| 4 | 0 | 90 | 10 | Gradient Start |
| 20 | 20 | 30 | 50 | Gradient End |
| 20.01 | 0 | 90 | 10 | Column Equilibration |
| 30 | 0 | 90 | 10 | End of Run |
| Class of Compounds | Vitamins |
| Analyzing Compounds | Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid), Nicotinamide, Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine), Folic Acid, Cyanocobalamin, Thiamine diphosphate (Thiamine pyrophosphate), Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5), Biotin |
Application Column
Chromni
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Cyanocobalamin
Folic Acid
Nicotinamide
Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid)
Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
Thiamine diphosphate (Thiamine pyrophosphate)
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)

HPLC Analysis of Active Drug in a Formulation
October 4, 2010
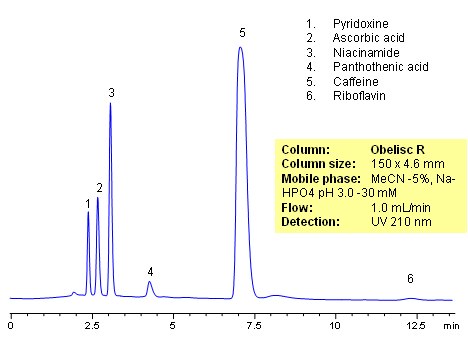
HPLC method for separation of active ingredients of drug/supplemental composition was developed on an Obelisc R trimodal HPLC column. Compounds are retained by combination of reversed-phase, cation-exchange and anion-exchange mechanisms. Compounds are well separated, and method can be used for quantitation of pyridoxine, ascorbic acid, niacinamide, pantothenic acid, caffeine and riboflavin in a mixture or as separate compounds in various complex mixtures. Various detection techniques can be applied for quantitation (ELSD, UV, LC/MS, Corona). This HPLC method can be adopted as general approach for analysis of active drug components in various formulations.
| Column | Obelisc R , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O -5/95% |
| Buffer | NaHPO4 pH 3.0 – 30 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 210 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Vitamin B₆, Hydrophobic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Pyridoxine, Ascorbic acid, Niacinamide, Pantothenic acid, Caffeine, Riboflavin |
Application Column
Obelisc R
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsAscorbic Acid
Caffeine
Niacinamide
Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)

HPLC Method for Separation of Vitamins Group B such as Nicotinic Acid, Pyridoxine, Niacinamide, Pantothenic Acid, Riboflavin on Obelisc N Column
August 22, 2008
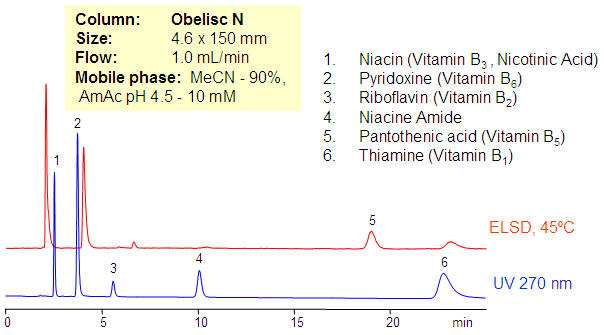
Separation of vitamins group B is achieved on Obelisc N column in HILIC mixed-mode. Vitamins of this group are different in polarity and ionic properties. Retention and separation is achieved by optimization of amount of ACN, buffer and buffer pH. Combination of UV and ELSD detection is used to monitor HPLC separation. B vitamins are water-soluble vitamins that play an important role in cell metabolism. Supplements containing all six are generally referred to as a vitamin B complex. Individual B vitamin supplements are referred to by the specific name of each vitamin. This method can be used to analyze individual B vitamins as well as vitamin B complex. Isolation of impurities as well as degradation products is possible by preparative chromatography.
| Column | Obelisc N , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmAC pH 4.5 – 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm, ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Vitamin B₆, Hydrophobic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Pyridoxine, Niacinamide, Pantothenic acid, Riboflavin |
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsNiacinamide
Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
UV Detection