| CAS Number | 7664-38-2 |
|---|---|
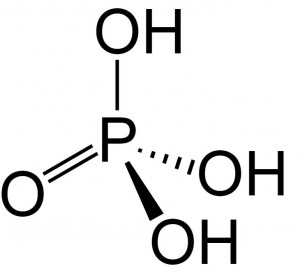
| Molecular Formula | H3O4P |
| Molecular Weight | 97.994 |
| InChI Key | NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -0.770 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
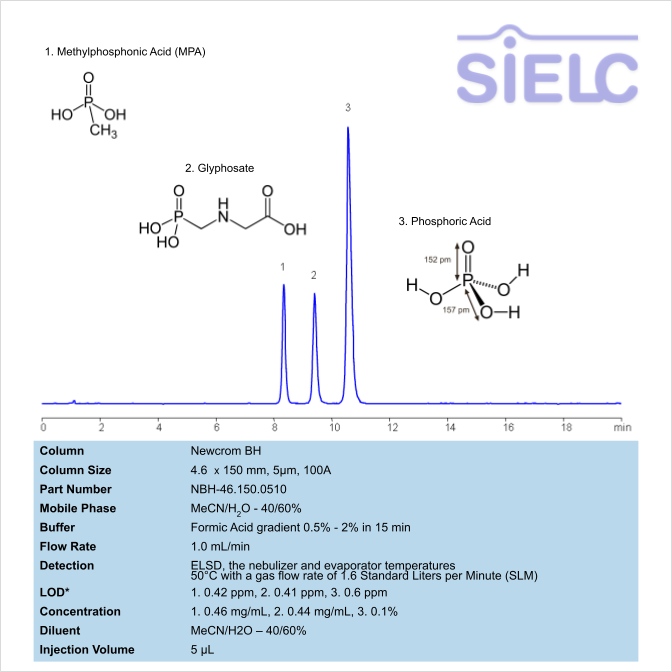
HPLC–ELSD Method for the Analysis of Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, and Phosphoric Acid Using a Newcrom BH Column
December 15, 2025
HPLC Method for Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, Phosphoric Acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, Phosphoric Acid.
Methylphosphonic acid is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula CH3P(OH)2. It is often used in some lubricant additives, textile treatments, and in synthesis of phosphonate compounds, like Glyphosate.
Glyphosate is an herbicide with a chemical formula of C3H8NO5P. It works through blocking enzymes, like 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase, essential for plant growth. It is typically found in agricultural work, but can occasionally be found in forestry and garden care. You can find detailed UV spectra of Glyphosate and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
Phosphoric acid is an inorganic compound with chemical formula H3PO4. It is odorless and colorless, which leads to it’s common use in soft drunks to help preserve the product. It is also used in fertilizers, metal treatment, and corrosion inhibition. Excessive intake of it is not recommended.
Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, Phosphoric Acid can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom BH stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a gradient method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a phosphoric acid buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 40/60% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid gradient 0.5% – 2% in 15 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 mL/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50°C with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| LOD* | 1. 0.42 ppm, 2. 0.41 ppm, 3. 0.6 ppm |
| Class of Compounds | Herbicides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, Phosphoric Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Methylphosphonic Acid
Phosphoric Acid

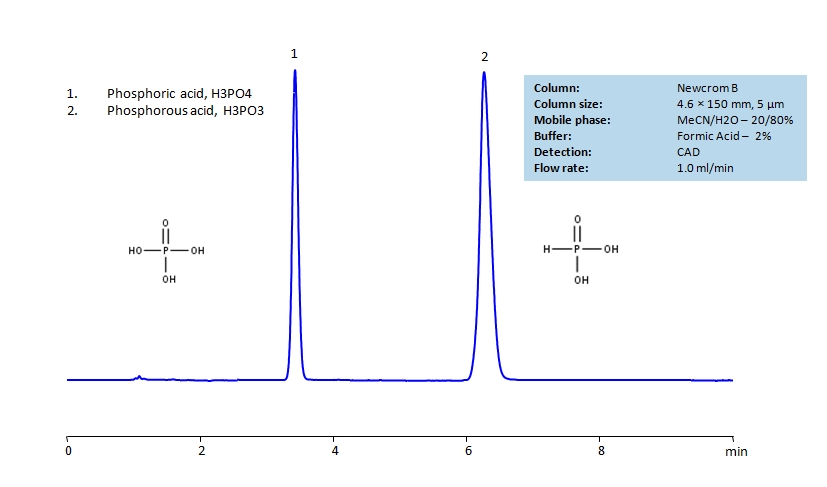
HPLC Separation of Phosphoric and Phosphorous Acids on Newcrom B Column
March 11, 2020
HPLC Method for Phosphoric Acid, Phosphorous acid on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Phosphoric Acid, Phosphorous acid.
Phosphoric acid is an inorganic compound with chemical formula H3PO4. It is odorless and colorless, which leads to it’s common use in soft drunks to help preserve the product. It is also used in fertilizers, metal treatment, and corrosion inhibition. Excessive intake of it is not recommended.
Phosphorous acid is a compound with chemical formula H3PO3. It’s most important use is considered to be the production of basic lead phosphite, which is a stabilizer in PVC. It is also used as a reducing agent and in the production of synthetic fibers, organophosphorus pesticides, and the water treatment agent ATMP.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid – 2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) MS- compatible mobile phase |
| Class of Compounds | Hydrophilic, Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Phosphoric Acid, Phosphorous acid |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Phosphorous acid

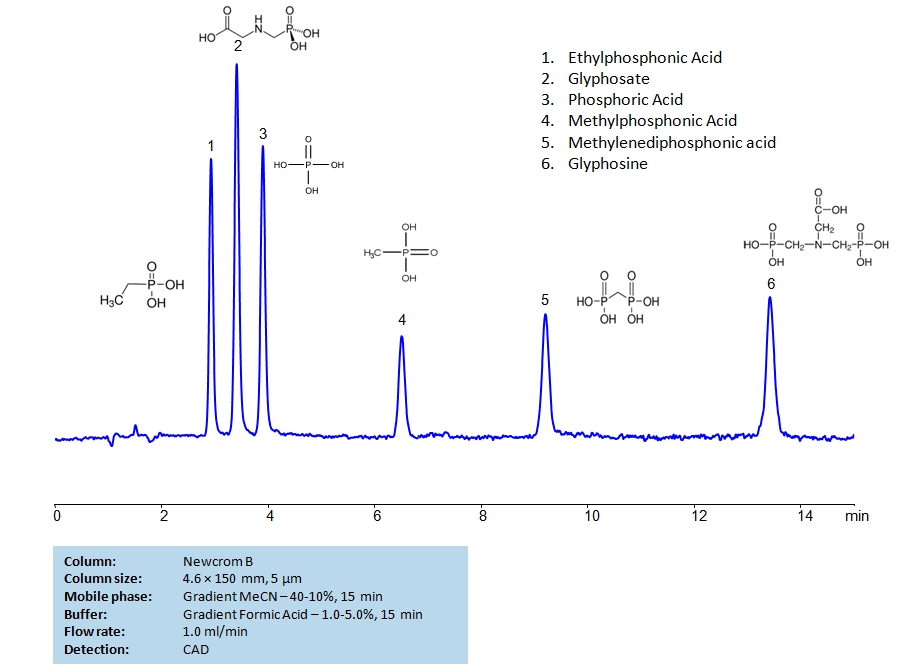
HPLC Separation of Glyphosate, Glyphosine, Ethylphosphonic, Methylphosphonic, Methylenediphosphonic and Phosphoric Acids on Newcrom B Column
December 4, 2019
HPLC Method for Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, Glyphosine, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, Glyphosine, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid.
Glyphosate is an herbicide with a chemical formula of C3H8NO5P. It works through blocking enzymes, like 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase, essential for plant growth. It is typically found in agricultural work, but can occasionally be found in forestry and garden care.
Glyphosine is a synthetic plant growth regulator with the chemical formula of C4H11NO8P2. It is a colorless liquid that works through decreasing chlorophyll production.
Ethylphosphonic acid has a C2H5P(O)(OH)2 chemical formula. It is typically found as white crystals or crystalline powder. It is often used as an internal standard when researching fosfomycin in human plasma as well as a synthetic nucleotide analog.
Methylphosphonic acid is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula CH3P(OH)2. It is often used in some lubricant additives, textile treatments, and in synthesis of phosphonate compounds, like the previously mentioned Glyphosate.
Methylenediphosphonic acid has the chemical formula CH2[P(O)(OH)2]2. It is typically seen as a precursor in synthesis of Mesoporous aluminum organophosphate, if alkyltrimethylammonium, and Tetraester of methylenediphosphonic acids.
Phosphoric acid is an inorganic compound with chemical formula H3PO4. It is odorless and colorless, which leads to it’s common use in soft drunks to help preserve the product. It is also used in fertilizers, metal treatment, and corrosion inhibition. Excessive intake of it is not recommended.
Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, Glyphosine, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom B stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a formic acid buffer. Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN Gradient -40-10%, 15 min |
| Buffer | Formic Acid Gradient -1- 5%, 15 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD |
| Class of Compounds | Acids, Plant growth regulator, Herbicide, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Glyphosate, Glyphosine, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Glyphosate
Glyphosine
Methylenediphosphonic acid
Methylphosphonic Acid
Phosphate
Phosphoric Acid

HPLC Separation of Ethylphosphonic, Methylphosphonic, Methylenediphosphonic and Phosphoric Acids on Newcrom B Column
December 2, 2019
HPLC Method for Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies  High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid
Ethylphosphonic acid has a C2H5P(O)(OH)2 chemical formula. It is typically found as white crystals or crystalline powder. It is often used as an internal standard when researching fosfomycin in human plasma as well as a synthetic nucleotide analog. Glyphosate is an herbicide with a chemical formula of C3H8NO5P. It works through blocking enzymes, like 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase, essential for plant growth. It is typically found in agricultural work, but can occasionally be found in forestry and garden care.
Methylphosphonic acid is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula CH3P(OH)2. It is often used in some lubricant additives, textile treatments, and in synthesis of phosphonate compounds, like the previously mentioned Glyphosate.
Methylenediphosphonic acid has the chemical formula CH2[P(O)(OH)2]2. It is typically seen as a precursor in synthesis of Mesoporous aluminum organophosphate, if alkyltrimethylammonium, and Tetraester of methylenediphosphonic acids. Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom B stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a formic acid buffer. Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/78% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid – 2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD |
| Class of Compounds | Acids, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Ethylphosphonic Acid, Methylphosphonic Acid, Methylenediphosphonic acid, Phosphate, Phosphoric Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Methylenediphosphonic acid
Methylphosphonic Acid
Phosphate
Phosphoric Acid

HPLC Separation of Phosphorous and Phosphoric Acids
July 10, 2012
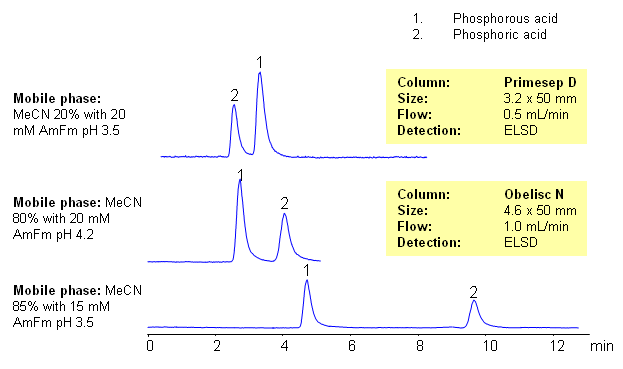
Application Notes: Phosphorus and phosphoric acid were separated on Obelisc N and Primesep D columns. On Obelisc N both acids retained by combination of HILIC and anion-exchange mechanisms. OnPrimesep D these inogranic acids are retained by anion-exchange mechanism. Both columns and methods can be used for analysis of hydrophilic organic and inorganic acids with multi-mode or single mode approach
Application Columns: Primesep D, Obelisc N
Application compounds: Phosphorous Acid, Phosphoric Acid
Detection technique: UV, LC/MS, ELSD/CAD
| Column | Primesep D, 3.2×50 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | ELCD |
| Column | Obelisc N, 4.6×50 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Fungicide, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Phosphorous Acid, Phosphoric Acids |
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsPrimesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsPhosphorous acid
UV Detection

HPLC Analysis of Basic Drugs and Acidic Counter-Ions by Mixed-Mode Chromatography
July 16, 2009
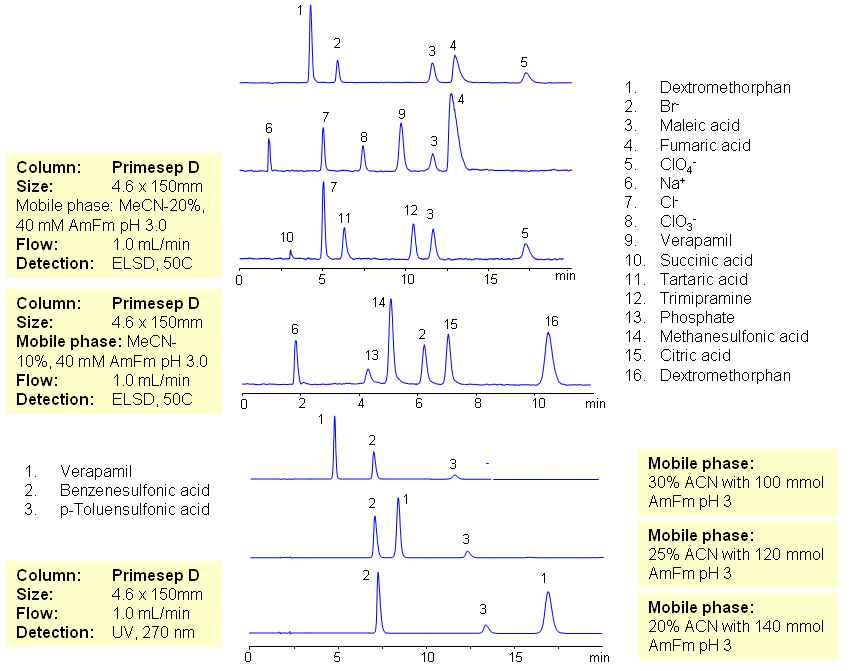
The majority of drugs in the pharmaceutical industry are administered in salt form. The presence of two counter-ions very often necessitates the use of two methods. The nature of these counterparts in drugs can be an inorganic cation and organic acid, inorganic anion and organic base, and organic cation and organic anion. Furthermore, the properties of the molecules will result in a differing stoichiometry. The task of simultaneous quantitation of counter-ions can be achieved by using mixed-mode columns. The general approach for analysis is based on properties of corresponding counter-ions. Hydrophobic basic drugs, like dextromethorphan, verapamil, trimipramine, and corresponding acidic counter-ions (chloride, chlorate, bromide, bromate, perchlorate, maleate, fumarate,tartrate, succinate, phosphate, citrate, benzosulfonate, toleuensulfonate) can be separated and quantitated in the same run on reversed-phase anion-exchange column. Basic hydrophobic drugs are retained by the reversed-phase mechanism, and counter-ions are retained by the reversed-phase and anion-exchange mechanism. Some polar counter-ions are retained only by the anion-exchange mechanism. Retention time and selectivity of HPLC separation of drugs and counter-ions can be achieved by changing the amount of acetonitrile and the amount of ions in the mobile phase. The detection technique depends on the properties of the counter-ions. In case of low or no UV activity, ELSD can be employed if the counter-ion forms a non-volatile salt with the mobile phase additive (ammonium formate). This HPLC method can be used for simultaneous quantitation of other basic drugs and counter-ions. The presence of two mechanisms of retention allows control over retention times of drug and counter-ion independently, and even allows a change of order of elution when necessary.
| Column | Primesep D , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, UV 270 |
| Class of Compounds | Ions, Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Base, Acids, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium Chloride, Sodium chloride, Sodium Chlorate, Sodium bromide, Sodium bromate, Perchloric Acid, Maleic Acid, Fumaric Acid, Tartaric Acid, Succinic Acid, Phosphoric Acid, Citric acid, Benzosulfonic acid, Dextromethorphan, Verapamil, Trimipramine |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsBromide
Chlorate
Chloride
Citric Acid
Dextromethorphan
Fumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Organic Acids
Perchlorate
Phosphoric Acid
Pyrilamine
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid
Verapamil
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)
UV Detection