| CAS Number | 7365-45-9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H18N2O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 238.301 |
| InChI Key | JKMHFZQWWAIEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -2.26 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
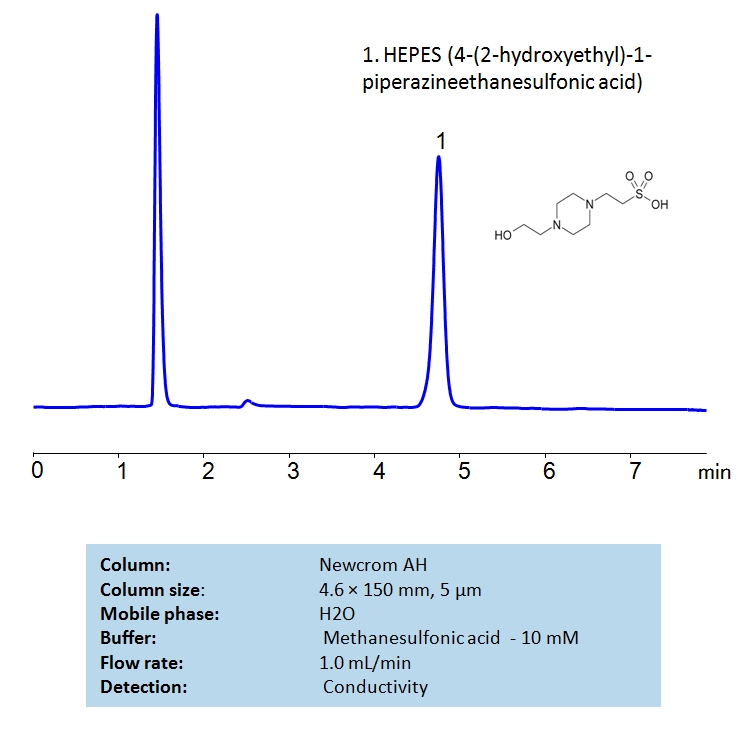
HPLC Determination of HEPES on Newcrom AH Column
October 20, 2020
HEPES is a zwitterionic organic chemical buffering agent. It is a very polar compound which is not retained by traditional reverse phase chromatography. HEPES can be separated by mixed-mode hydrophilic interaction chromatography on the Newcrom AH mixed-mode column, which has both hydrophobic and cationic exchange properties. The mobile phase consists of H2O and Methanesulfonic acid. It can be detected using a conductivity detector.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | H2O- 100% |
| Buffer | Methanesulfonic acid – 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | Conductivity |
| Class of Compounds |
Hydrophilic |
| Analyzing Compounds | HEPES |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options
Effect of Buffer on HPLC Separation of Buffers
August 22, 2008
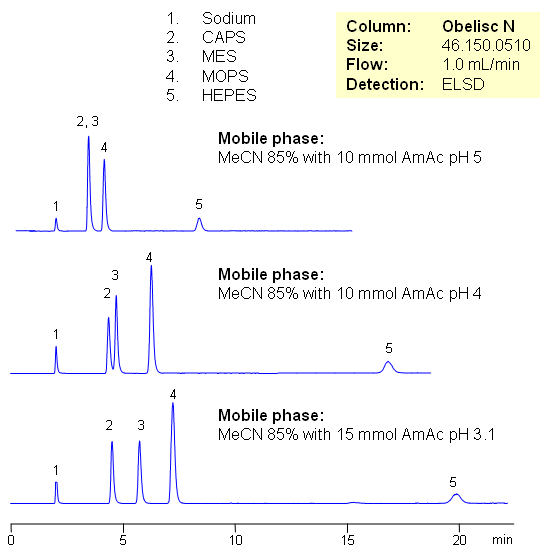
HEPES, CAPS, MES and MOPS are zwitterionic organic chemical buffering agents. These are very polar compounds which are not retained by traditional reverse phase chromatography. These compounds are zwitterions in nature and can be separated by mixed-mode hydrophilic interaction chromatography on Obelisc N column. Retention is achieved by combination of HILIC and ion-exchange mechanisms. These buffering agents do not have UV active groups, but can be analyzed with ESLD, LC/MS, and CAD detection.
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select options4-Morpholinepropanesulfonic Acid (MOPS)
CAPS (3-(Cyclohexylamino)propanesulfonic acid)
HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic Acid)
Zwitterion