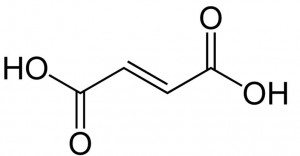
| CAS Number | 110-17-8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 116.072 |
| InChI Key | VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N |
| LogP | -0.480 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of Fumaric Acid
August 5, 2025
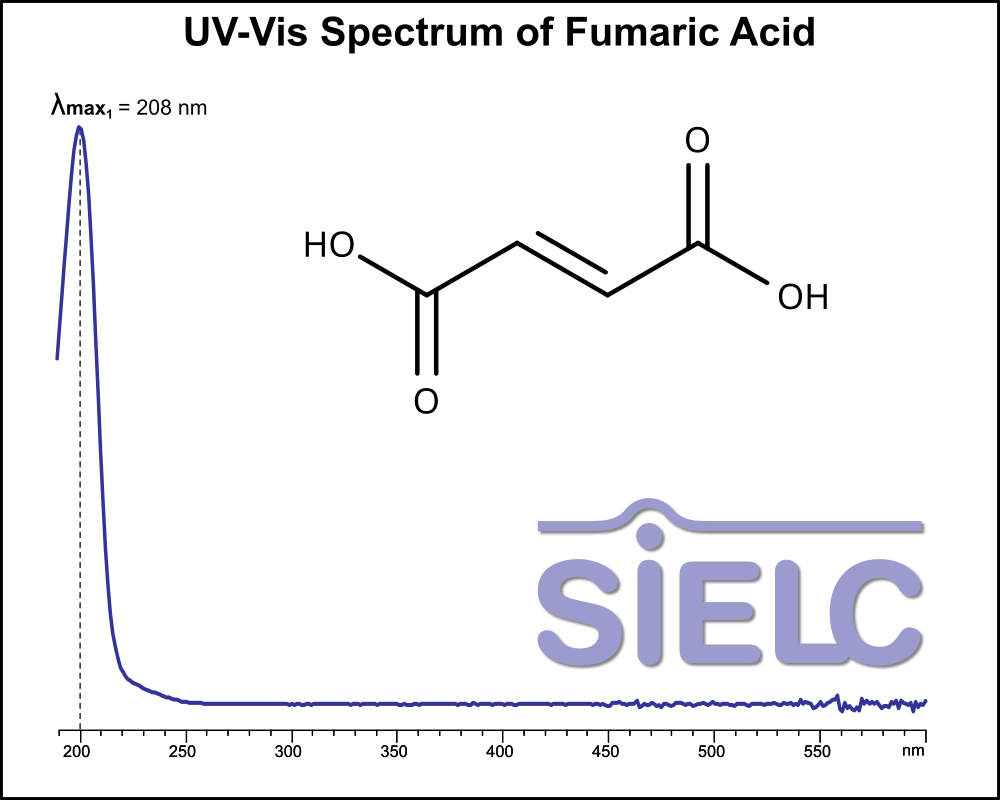
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC Method for Analysis of Maleic acid, Ascorbic acid, Nicotinic acid, Fumaric acid and Oxalic acid on BIST™ A+ Column
July 8, 2022
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
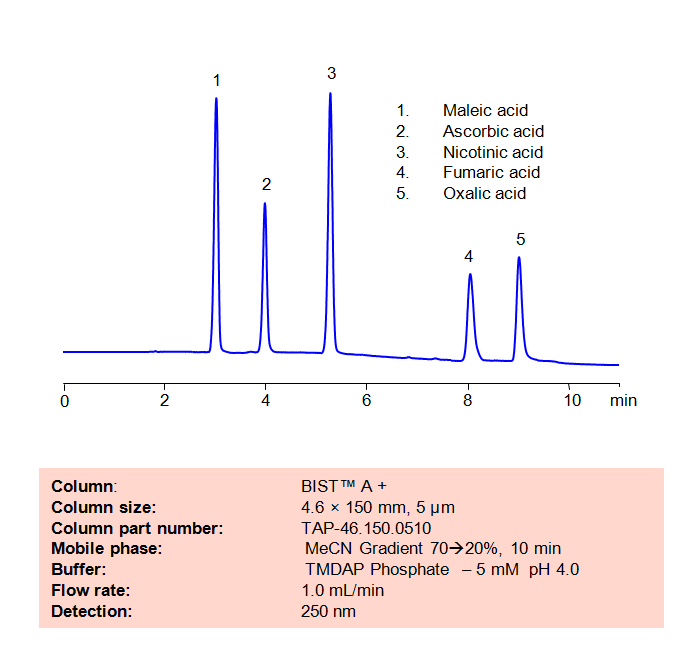
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Maleic acid, Ascorbic acid, Nicotinic acid, Fumaric acid and Oxalic acid
The maleate ion from Maleic acid is a popular ingredient as the maleate salt in several different drugs, including Methergine, Pyrilamine, and Carfenazine, among others. Nicotinic acid, also known as Niacin or Vitamin B3, is an essential nutrient for the human body and is sometimes taken as a treatment for high cholesterol. Aconitic acid is a key intermediary in the citric acid cycle, and is also used a flavoring agent and in the production of rubbers and plastics. Fumaric acid is a popular preservative and food additive with a fruit-like taste. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, a mixture of these organic acids can be separated on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A+ column, contrary to conventional chromatographic wisdom. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine (TMDAP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include Calcium acetate and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, these organic acids can be separated, retained, and detected through ELSD. This method is also compatible with Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and CAD.
Condition
| Column | BIST™ A+, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN Gradient |
| Buffer | TMDAP ( N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-diaminopropane) phosphate – 5 mM pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 250 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acids, Organic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Maleic acid, Ascorbic acid, Nicotinic acid, Fumaric acid and Oxalic acid |
Application Column
BIST A+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid)
Oxalic Acid

HPLC Method for Analysis of Maleic Acid, Nicotinic Acid, Aconitic Acid and Fumaric Acid on BIST™ A+ Column
July 7, 2022
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
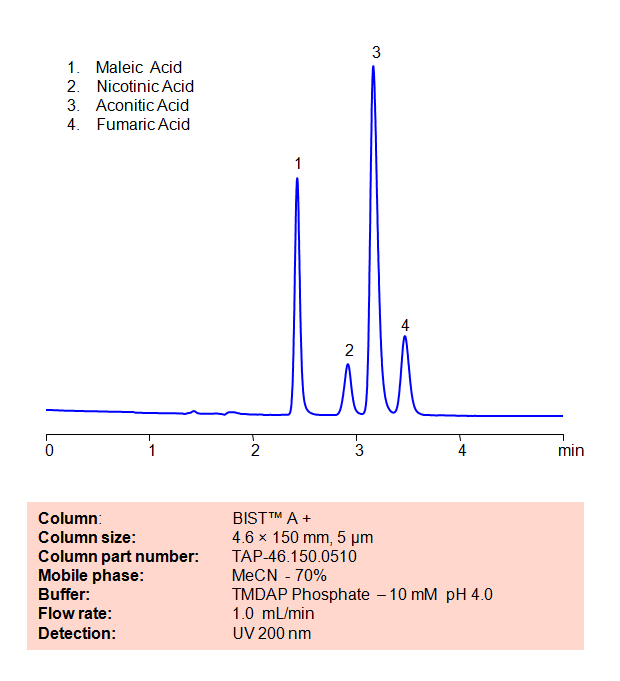
The maleate ion from Maleic acid is a popular ingredient as the maleate salt in several different drugs, including Methergine, Pyrilamine, and Carfenazine, among others. Nicotinic acid, also known as Niacin or Vitamin B3, is an essential nutrient for the human body and is sometimes taken as a treatment for high cholesterol. Aconitic acid is a key intermediary in the citric acid cycle, and is also used a flavoring agent and in the production of rubbers and plastics. Fumaric acid is a popular preservative and food additive with a fruit-like taste. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, a mixture of these organic acids can be separated on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A+ column, contrary to conventional chromatographic wisdom. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine (TMDAP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes.
Condition
| Column | BIST™ A+, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 70% |
| Buffer | TMDAP ( N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-diaminopropane) Phosphate – 10 mM pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Dicarboxylic acid, Tricarboxylic acid, Pyridinecarboxylic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Maleic Acid, Nicotinic Acid, Aconitic Acid, Fumaric Acid |
Application Column
BIST A+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Nicotinic Acid/Niacin (3-pyridinecarboxylic acid)
trans-Aconitic acid

HPLC Separation of Sorbic, Fumaric, Malonic Acids on Newcrom BH Column
June 25, 2020
Acids with different strengths can be retained and elution order controlled by the use of a mixed-mode column, which has an ion-exchange component in addition to hydrophobic retention. In this example, the Newcrom BH mixed-mode column was used to separate fumaric, malonic and sorbic acids in HPLC. Sorbic acid was mostly retained by hydrophobicity, while fumaric and malonic acids were also retained by the adjustment strength of the mobile phase
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sorbic Acid, Levulinic Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select optionsMalonic Acid
Sorbic acid

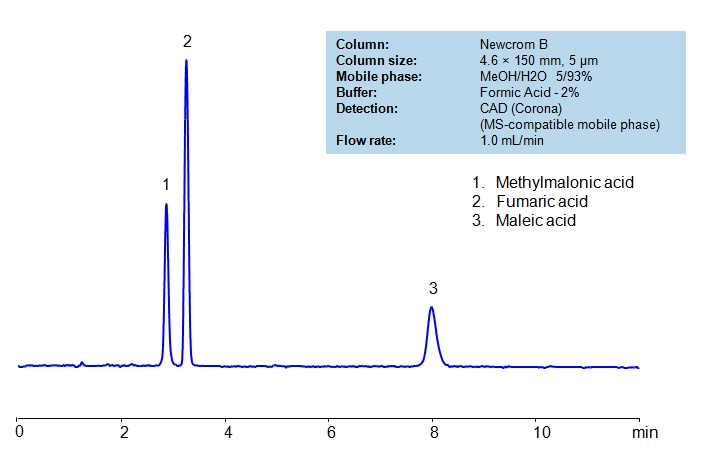
HPLC Separation of Methylmalonic, Fumaric, Maleic acids on Newcrom B Column
October 28, 2019
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeOH/H2O – 5/93% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid – 2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) (MS-compatible mobile phase) |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Methylmalonic acid, Fumaric acid, Maleic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom B
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select optionsMaleic Acid
Methylmalonic Acid

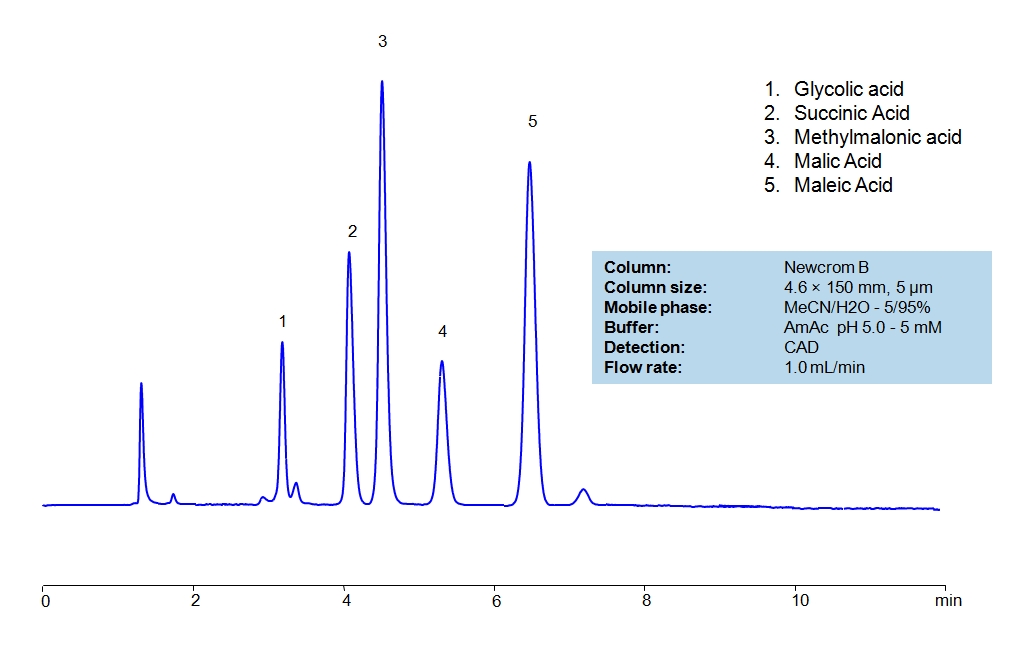
HPLC Separation of Small Organic Acids on Newcrom B Column
October 22, 2019
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 5/95% |
| Buffer | AmAc pH 5.0, Formic Acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) MS- compatible mobile phase |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Glycolic acid, Succinic Acid, Methylmalonic acid, Malic Acid, Maleic Acid, Citric Acid, Tartaric Acid, Fumaric Acid, Malonic Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom B
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Gluconic acid
Glycolic acid
Maleic Acid
Malic Acid
Malonic Acid
Methylmalonic Acid
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid
dl-Tartaric acid

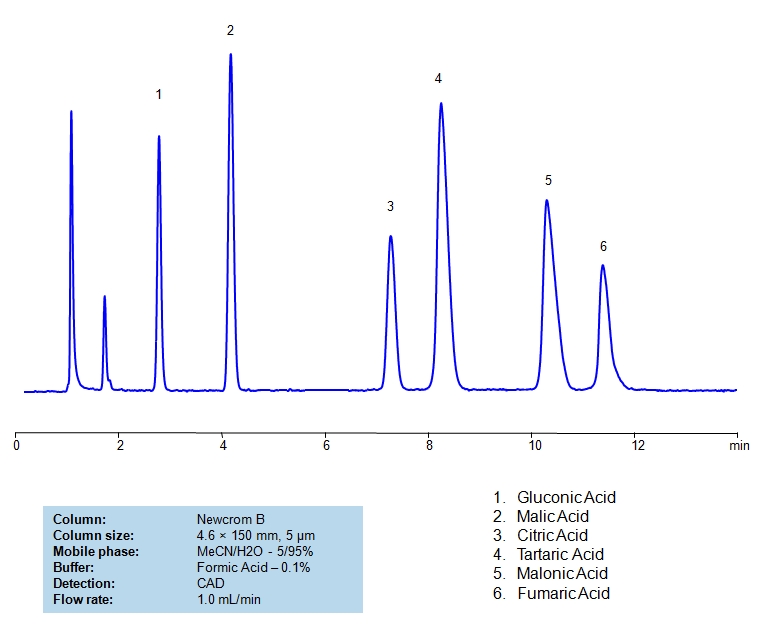
Separation of Compounds in TCA Cycle on Primesep D Column
July 3, 2013
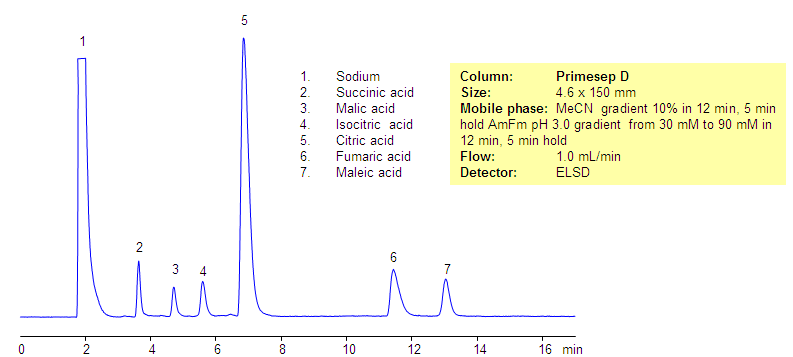
The citric acid cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle, Krebs cycle) is a key process in the metabolic pathway by which all aerobic organisms generate energy. Compounds generated during TCA are hydrophilic, acidic compounds. Some of the hydrophilic acids are very strong while others are relatively weaker. All compounds have very low hydrophobicity and do not retain by the reversed-phase mechanism on the C18 or C8 HPLC columns. Citric acid and related products were separated in reversed-phase, anion-exchange mode on the Primesep D mixed-mode column. All hydrophilic, acidic compounds are well separated and demonstrate good shape. This robust method can be used for analysis of components of the TCA cycle and other highly hydrophilic compounds. This method is fully compatible with LC/MS and prep chromatography.
| Column | Primesep D, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm, pH 3.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium, Succinic acid, Malic acid, Isocitric acid, Citric acid, Fumaric acid, Maleic acid |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Isocitric Acid
Maleic Acid
Malic Acid
Sodium
Succinic Acid

Analysis of Compounds of TCA Cycle on SHARC 1 Column
July 2, 2013
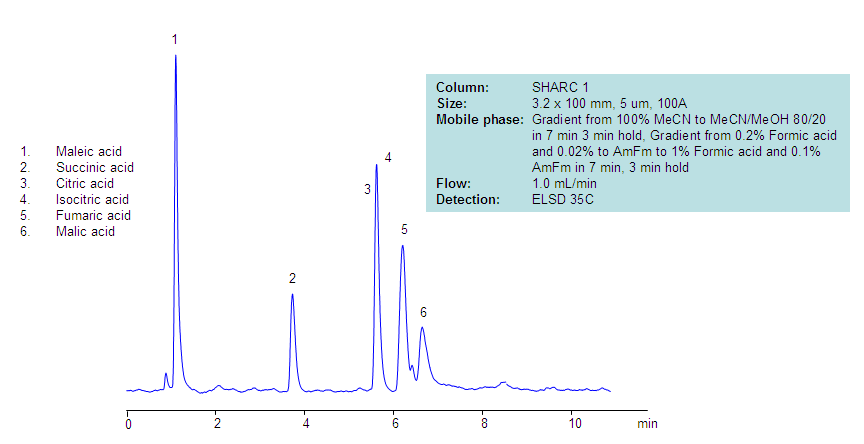
This is an alternative approach for the separation of the TCA cycle intermediates that was developed using novel hydrogen-bonding HPLC column. The organic nature of the mobile phase helps obtain a highly sensitive LC/MS compatible method.
Application Column
SHARC 1
The SHARC™ family of innovative columns represents the first commercially available columns primarily utilizing separation based on hydrogen bonding. SHARC stands for Specific Hydrogen-bond Adsorption Resolution Column. Hydrogen bonding involves an interaction or attraction between a bound hydrogen atom and molecules containing electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Isocitric Acid
Maleic Acid
Malic Acid
Succinic Acid

HPLC Analysis of Basic Drugs and Acidic Counter-Ions by Mixed-Mode Chromatography
July 16, 2009
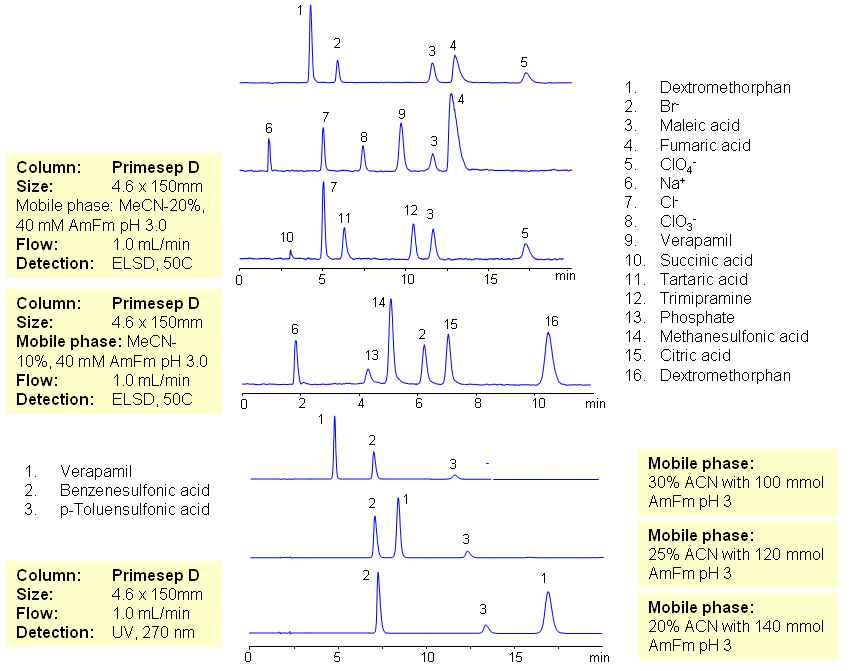
The majority of drugs in the pharmaceutical industry are administered in salt form. The presence of two counter-ions very often necessitates the use of two methods. The nature of these counterparts in drugs can be an inorganic cation and organic acid, inorganic anion and organic base, and organic cation and organic anion. Furthermore, the properties of the molecules will result in a differing stoichiometry. The task of simultaneous quantitation of counter-ions can be achieved by using mixed-mode columns. The general approach for analysis is based on properties of corresponding counter-ions. Hydrophobic basic drugs, like dextromethorphan, verapamil, trimipramine, and corresponding acidic counter-ions (chloride, chlorate, bromide, bromate, perchlorate, maleate, fumarate,tartrate, succinate, phosphate, citrate, benzosulfonate, toleuensulfonate) can be separated and quantitated in the same run on reversed-phase anion-exchange column. Basic hydrophobic drugs are retained by the reversed-phase mechanism, and counter-ions are retained by the reversed-phase and anion-exchange mechanism. Some polar counter-ions are retained only by the anion-exchange mechanism. Retention time and selectivity of HPLC separation of drugs and counter-ions can be achieved by changing the amount of acetonitrile and the amount of ions in the mobile phase. The detection technique depends on the properties of the counter-ions. In case of low or no UV activity, ELSD can be employed if the counter-ion forms a non-volatile salt with the mobile phase additive (ammonium formate). This HPLC method can be used for simultaneous quantitation of other basic drugs and counter-ions. The presence of two mechanisms of retention allows control over retention times of drug and counter-ion independently, and even allows a change of order of elution when necessary.
| Column | Primesep D , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, UV 270 |
| Class of Compounds | Ions, Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Base, Acids, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium Chloride, Sodium chloride, Sodium Chlorate, Sodium bromide, Sodium bromate, Perchloric Acid, Maleic Acid, Fumaric Acid, Tartaric Acid, Succinic Acid, Phosphoric Acid, Citric acid, Benzosulfonic acid, Dextromethorphan, Verapamil, Trimipramine |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsBromide
Chlorate
Chloride
Citric Acid
Dextromethorphan
Fumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Organic Acids
Perchlorate
Phosphoric Acid
Pyrilamine
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid
Verapamil
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)
UV Detection

HILIC Separation of Carboxylic Acids
August 22, 2008
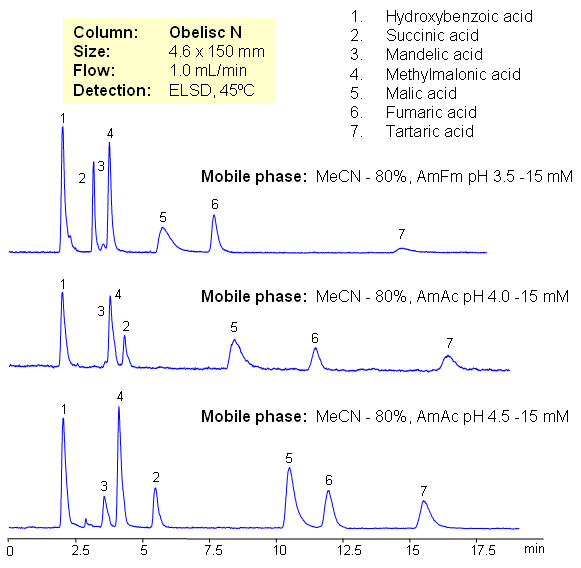
Hydrophilic acids are separated on Obelisc N mixed-mode HILIC column. Seven carboxylic acids are separated based on their polarity and pKa values. Changes in ionization states of acids and stationary phase can be used to control elution order of organic and inorganic acids.
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsHydroxybenzoic Acid
Malic Acid
Mandelic Acid
Methylmalonic Acid
Organic Acids
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid

HPLC Separation of Organics Acids
November 21, 2006
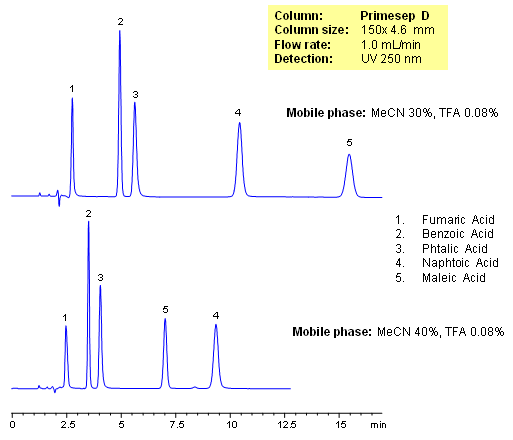
Primesep D separates organic acids such as fumaric, benzoic, phthalic, naphthoic, and maleic acids by a mixture of anion exchange and reversed phase. Retention times and elution order can be changed by adjusting the percentage of acetonitrile in the mobile. This can not be done by traditional ion-exchange and ion-exclusion chromatography. The HPLC separation uses a mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN) and trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) and UV detection at 250 nm.
| Column | Primesep D, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Fumaric Acid, Benzoic Acid, Phthalic Acid, Maleic Acid, Naphtoic Acid |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Naphthoic Acid
Organic Acids
Phthalic Acid

Separation of Diacid Hydrophobic and Ion Exchange Modes
October 11, 2005
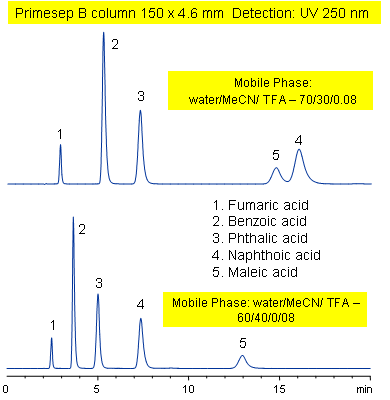
Primesep B combines a hydrophobic, reversed-phase mechanism with ion exchange to separate the diacids, fumaric, benzoic, phthalic, naphthoic, and maleic acids. Changing the acetonitrile content of the mobile phase reverses the peak order for naphthoic and maleic acids. Primesep B combines reversed-phase and anion-exchange mechanism with a mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN) and trifluoracetic acid (TFA) and UV detection at 250 nm.
| Column | Primesep B, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | TFA |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 250 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Fumaric acid, Benzoic acid, Phthalic acid, Naphthoic acid, Maleic acid, ) |
Application Column
Primesep B
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsDicarboxylic Acids
Fumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Naphthoic Acid
Phthalic Acid

Separation of Diacid Hydrophobic and Ion Exclusion Modes
October 4, 2005
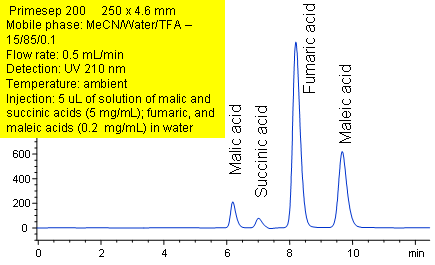
Primesep 200 retains and separates the organic diacids (malic, succinic, fumaric, and maleic) by a combination hydrophobic, reversed-phase interactions and ion exclusion. The separation uses a mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN) and trifluoracetic acid (TFA) with UV detection at 210 nm.
Application Column
Primesep 200
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Malic Acid
Succinic Acid

Separation of Diacid: Ion Exclusion mode
August 6, 2003
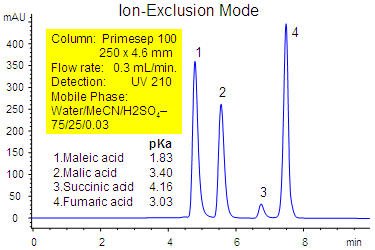
Primesep 100 separates a mixture of dicarboxylic acids in ion-exclusion mode with a mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN, ACN), and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) with UV detection at 210 nm. Baseline resolution of fumaric, maleic, malic, and succinic acids is obtained in less than 8 minutes. The separation combines ion-exclusion and reversed-phase mechanisms in one method.
Application Column
Primesep 100
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsFumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Malic Acid
Succinic Acid