| CAS Number | 56-75-7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H12Cl2N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 323.131 |
| InChI Key | WIIZWVCIJKGZOK-RKDXNWHRSA-N |
| LogP | 1.14 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
HPLC Analysis of Chloramphenicol
July 31, 2015

Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic useful in treating conjunctivitis and many other infections. It is notable as an antibiotic for developing nations due to its low cost. It was analyzed on a Legacy L1 column which uses reverse-mode to retain hydrophobic compounds. Comparisons between Legacy L1 and Phenomenex columns are available upon request.
| Column | Legacy L1, 4.6×250 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeOH – 45% |
| Buffer | Acetic Acid – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 280 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Antibiotics, Hydrophobic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Chloramphenicol |
&
Application Column
Legacy L1
SIELC's family of Legacy columns is based on the United States Pharmacopeia's (USP) published chromatographic methods and procedures. Numerous brands have columns used in USP reference standards and methods. USP has created various designations to group together columns with similar types of packing and properties in the solid phase. SIELC's Legacy columns adhere to these strict requirements and properties, allowing you to easily replace older columns that are no longer available without needing to significantly modify your method or SOPs.
Select options
USP Methods for Chloramphenicol using a Legacy L1 Column
June 21, 2012
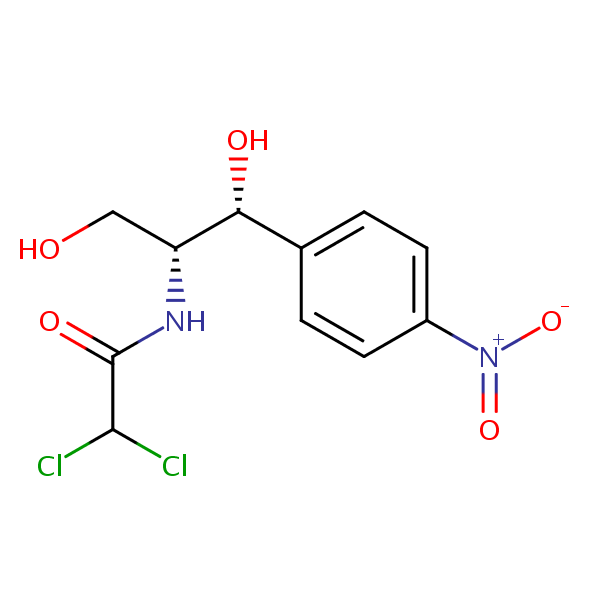
Application Notes: Chloramphenicol is a common broad spectrum antibiotic developed in the 1940’s. According to the USP methods, chloramphenicol should contain no less than 97.0% and no more than 103% of chloramphenicol calculated on a dried basis. The USP HPLC method for the analysis of chloramphenicol was developed on Legacy L1 column according to the US Pharmacopeia methodology. L1 classification is assigned to reversed-phase HPLC column containing C18 ligand. Support for the material is spherical silica gel with particles size 3-10 um and pore size of 100-120A.
Application Columns: Legacy L1 C18 HPLC column
Application compounds: Chloramphenicol
Mobile phase: MeOH/H2O/AcOH 45/55/0.1
Detection technique: UV
Reference: USP 30: NF35
| Column | Legacy L1, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeOH/H2O/AcOH 45/55/0.1 |
| Buffer | AcOH |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 270 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Hydrophobic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Chloramphenicol |
Application Column
Legacy L1
SIELC's family of Legacy columns is based on the United States Pharmacopeia's (USP) published chromatographic methods and procedures. Numerous brands have columns used in USP reference standards and methods. USP has created various designations to group together columns with similar types of packing and properties in the solid phase. SIELC's Legacy columns adhere to these strict requirements and properties, allowing you to easily replace older columns that are no longer available without needing to significantly modify your method or SOPs.
Select options
HPLC Separation of Antibiotics in Fish Production
August 22, 2008
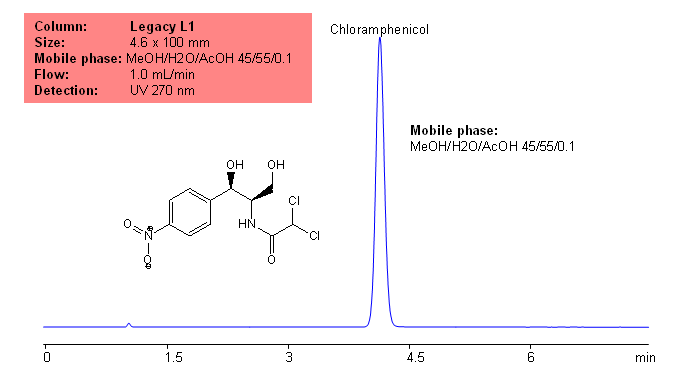
Five antibiotics are separated on Primesep C mixed-mode cation-exchange column using UV, ESLD and LC/MS compatible conditions. Similar compounds can be separated based on reverse phase and cation-exchange mechanisms. Current method can be used in quantitative determination of antibiotics in various food products.
Application Column
Primesep C
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsChloramphenicol
Furaltadone
Furazolidone
Nitrofurantoin

HPLC Separation of Common Antibiotics in Fish Farming
December 6, 2007
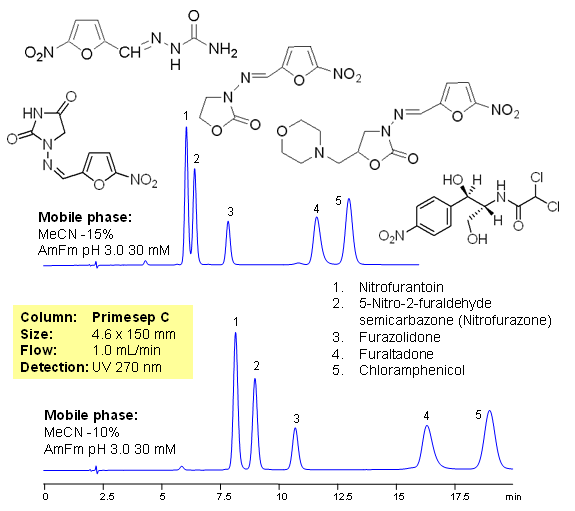
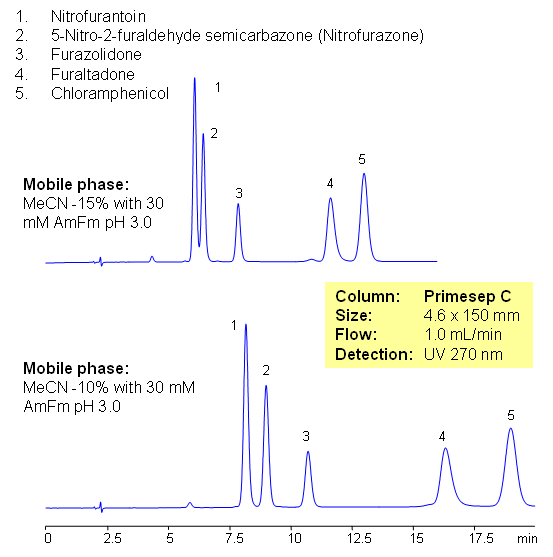
Fish antibiotics are used in fish farming to treat bacterial diseases of fish. It is common practice in the fish industry, particularly in developing countries, to use large amounts of antibiotics to prevent infection. The antibiotics used are often non-biodegradable and remain in the environment for long periods of time, contaminating soil and ground waters. In farming antibiotics are mixed with food and residual amount of drugs ends up in fish products and poultry, this lead to consumption of antibiotics and metabolites by humans. Five common antibiotics are separated on Primesep C column using LC/MS compatible conditions. Method can be used for quantitative determination of nitrofurantoin, nitrofurazone, furazolidone, furaltadone, chloramphenicol and nitrofurazone in fish products and environment.
Application Column
Primesep C
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsChloramphenicol
Furaltadone
Furazolidone
Nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurazone